- Baby Clothes
- Children’s Clothes
- Ethnic Clothing
- Men’s Clothing
- Wedding Guest Dresses
- Women’s Clothing
- Muslim Clothing
- Women’s Shirts
- Women’s Dresses
- Women’s Suits Sets
- Women’s Coats & Jacket
- Women’s Hoodies & Sweatshirts
- Women’s Jumpsuits
- Women’s Pyjamas
- Women’s Trousers
- Women’s Short Sleeve T-shirts
- Women’s Skirts
- Women’s Blazers & Suit Jackets
- Women’s Sweaters
- Women’s Tops
- Women’s Lingerie & Underwear
- Women’s Vests
- Women’s Yoga Clothing & Pilates Wear
Description

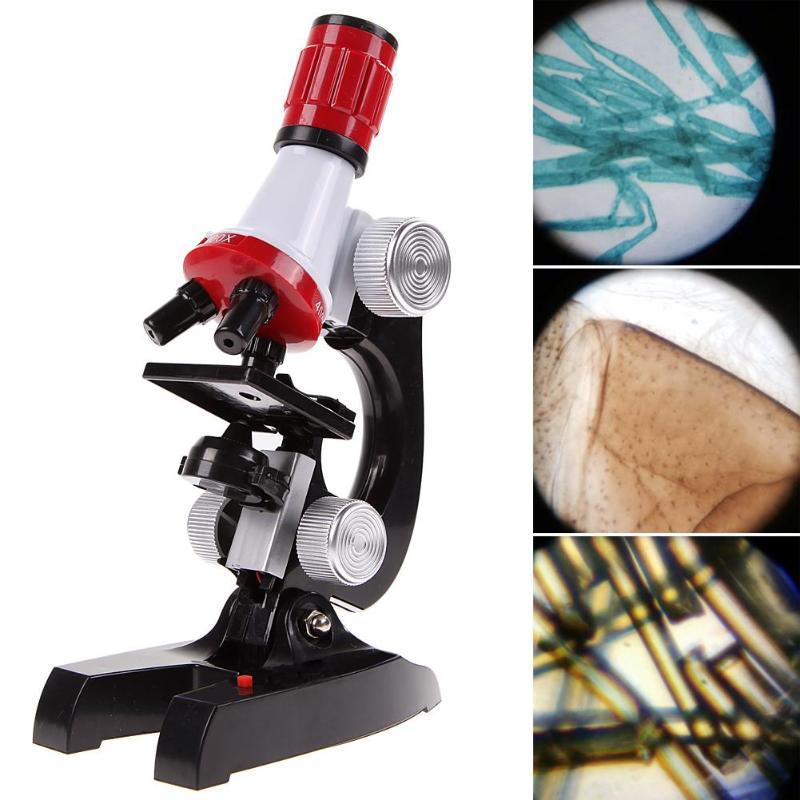
Microscope – Discover the World at a Micro Level
A microscope is an essential tool for anyone who is fascinated by the microscopic world. Whether you’re a student, researcher, hobbyist, or simply curious about the tiny world around us, a microscope opens up a new realm of exploration. With a microscope, you can magnify the smallest details and reveal the hidden structures of everyday objects, cells, and organisms that are invisible to the naked eye.
From biology students studying cells to engineers examining materials, microscopes are used in a variety of fields for scientific research, education, and even entertainment. This guide will introduce you to the features, benefits, and different types of microscopes available, helping you make an informed decision about which microscope best suits your needs.
Why You Need a Microscope
The microscopic world is filled with fascinating organisms, textures, and structures that we often take for granted. Having a microscope allows you to explore this world in detail, whether you’re studying biology, conducting experiments, or simply indulging your curiosity. Here are some of the key reasons why a microscope is an indispensable tool:
-
Scientific Exploration: Whether you’re in a classroom, laboratory, or at home, a microscope is a tool for scientific discovery. It’s used in various fields such as biology, chemistry, physics, and material science to study organisms, molecules, and structures at a magnified level.
-
Educational Tool: Microscopes are crucial in schools and universities, especially for students studying biology, anatomy, or any field that involves the study of tiny organisms or microscopic phenomena. It’s one of the most effective ways to bring theory to life by providing hands-on learning experiences.
-
Professional Use: Researchers, doctors, and professionals in fields like medicine, forensics, and engineering rely on microscopes for analyzing samples, diagnosing diseases, and investigating materials for further study and development.
-
Home Exploration: A microscope is also perfect for at-home exploration. Kids can use it to study tiny creatures like insects, plants, or even everyday objects such as hair and dust particles. It fosters curiosity and enhances the learning experience.
Types of Microscopes
When considering a microscope, it’s important to understand the different types and how they serve distinct purposes. The main types of microscopes include:
1. Optical (Light) Microscopes
Optical microscopes, also known as light microscopes, are the most common and widely used type. They use visible light and lenses to magnify objects. Optical microscopes come in several forms:
-
Monocular Microscopes: These microscopes have a single eyepiece, making them suitable for beginners and students.
-
Binocular Microscopes: With two eyepieces, these microscopes are more comfortable for prolonged use and offer a better 3D view of the sample.
-
Compound Microscopes: This is the most common optical microscope, featuring multiple lenses (objectives) to achieve higher magnification levels, typically ranging from 40x to 1000x.
-
Stereo (Dissecting) Microscopes: These are ideal for viewing larger objects at lower magnifications, such as insects, leaves, or small mechanical parts.
2. Electron Microscopes
Unlike optical microscopes, electron microscopes use a beam of electrons rather than light to create an image. This enables much higher magnification, allowing scientists to see objects as small as individual molecules or atoms.
-
Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM): TEMs pass electrons through a thin sample to create detailed images of internal structures at extremely high magnifications (over 1,000,000x).
-
Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM): SEMs provide 3D images of the surface of a sample by scanning it with a focused electron beam. SEMs are commonly used in research and material science.
3. Digital Microscopes
Digital microscopes combine optical and electronic technology. These microscopes feature built-in cameras that allow users to capture and record images and videos of the sample. The digital output can be displayed on a computer or screen for easier viewing, analysis, and sharing. Digital microscopes are widely used in educational settings, as well as by professionals in laboratories.
Key Features of a Good Microscope
When choosing a microscope, there are several key features to consider. These include magnification power, illumination, build quality, and additional features such as cameras or computer connectivity. Here are the main features to look for:
1. Magnification Power
The magnification power of a microscope determines how much larger the object will appear compared to its actual size. The magnification is usually indicated by a number followed by an “x,” such as 40x or 1000x.
-
Low Magnification (up to 100x): Suitable for viewing larger specimens such as insects or plant structures.
-
Medium Magnification (100x to 400x): Ideal for studying smaller objects such as cells or microorganisms.
-
High Magnification (above 1000x): Best for looking at very small structures like bacteria or detailed tissue samples.
2. Illumination
Adequate illumination is essential for clear and bright images. Most modern microscopes come with built-in LED lighting, which is adjustable to suit different magnifications. Some models offer both transmitted light (light passing through the sample) and reflected light (light bouncing off the surface of the sample).
3. Objective Lenses
The objective lenses are the primary lenses used to magnify the sample. Higher-quality microscopes will have several objective lenses with varying magnifications. Common objectives include 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x.
4. Focus Mechanism
Microscopes typically have coarse and fine focus knobs. The coarse focus is used for quick adjustments, while the fine focus is used for precise focusing at higher magnifications.
5. Build Quality and Stability
A microscope should have a solid build to ensure stability while using it. It should have a sturdy base and a metal frame for durability. High-quality microscopes are often made with materials like aluminum or stainless steel.
Applications of Microscopes
Microscopes have a vast range of applications across various fields:
-
Education: Microscopes are widely used in schools and universities to teach students about biology, anatomy, physics, and materials science. They help bring textbook concepts to life by offering practical learning experiences.
-
Healthcare: In medical laboratories, microscopes are essential for diagnosing diseases, studying cells, and researching pathogens.
-
Research: Scientists use microscopes to conduct research in fields like microbiology, biotechnology, and materials science, studying everything from cells and viruses to crystals and fibers.
-
Forensics: Microscopes play a crucial role in forensic science, helping experts examine tiny samples like hair, fibers, or trace evidence found at crime scenes.
-
Hobbyists: Amateurs and hobbyists can use microscopes to explore the world of insects, plants, and crystals, fostering curiosity and hands-on learning.
Conclusion
A microscope is not just a tool; it’s a gateway to a world of discovery. Whether you’re a student studying biology, a researcher analyzing cells, or a curious mind exploring the wonders of nature, a microscope opens up new possibilities. With various types, magnification powers, and features available, you can find the perfect microscope to suit your needs.
Invest in a high-quality microscope and embark on an exciting journey into the microcosmic world. Whether you’re using it for scientific research, educational purposes, or personal exploration, a microscope will enhance your understanding of the world in ways you never imagined.









Additional information
| Weight | 0.360 kg |
|---|---|
| Color |
Black |
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Microscope” Cancel reply
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
A dinosaur track racing toy suitable for children aged 3-5, creating a dinosaur world road race with a flexible track toy set
28.22$ – 44.62$
A dinosaur track racing toy suitable for children aged 3-5, creating a dinosaur world road race with a flexible track toy set
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Automatic Electric Bubble Gun with 64 Holes
53.00$
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
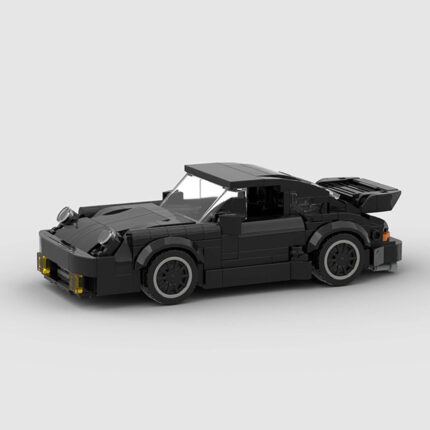
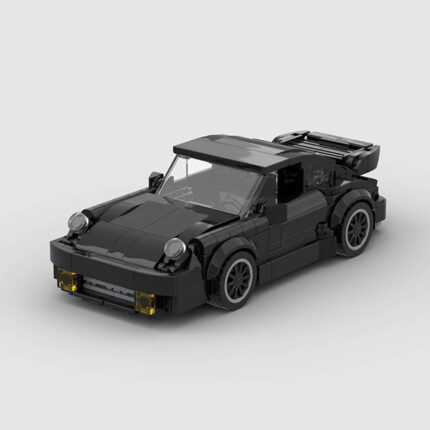
Building Blocks Compatible With Lego 83496 Black Porsche 911Turbo Creative Educational Children’s Toys Assembling
48.78$
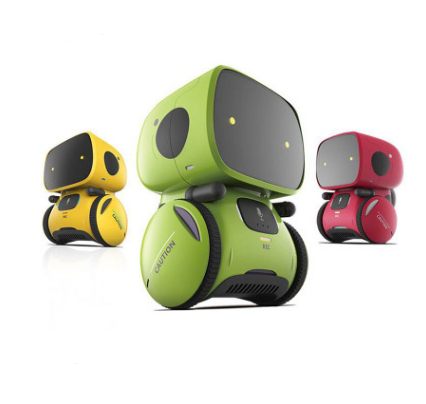
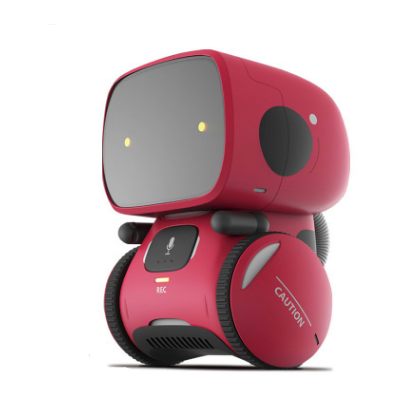
Children Voice Recognition Robot Intelligent Interactive Early Education Robot
30.45$
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
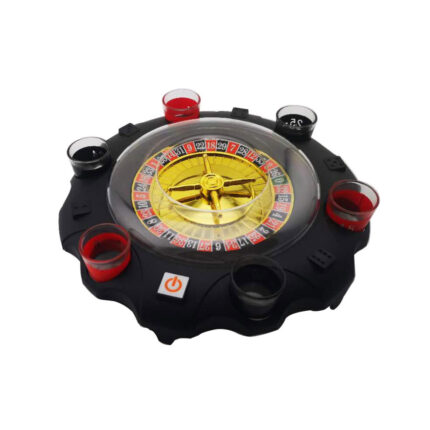
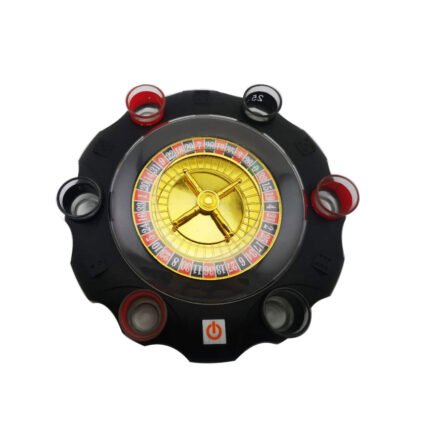
Roulette Wine Set Turntable Turn Music Drinking Game KTV Bar Nightclub Electric Russian Lucky Turntable
22.00$
Wireless Remote Control Double-sided Driving Stunt Car 4WD 360 Degree Rotation Toy
28.14$
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page





























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.